Main Model

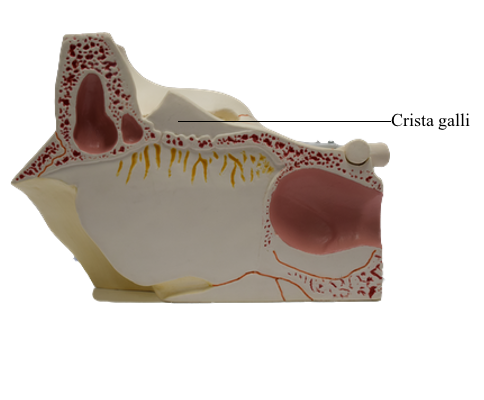
Orbit : 27 Crista galli
Anterior Cranial Fossa
The inferior and anterior parts of the frontal lobes of the brain
occupy the anterior cranial fossa, the shallowest of the three
cranial fossae. The fossa is formed by the frontal bone anteriorly, the ethmoid bone in the middle, and the body
and lesser wings of the sphenoid posteriorly. The greater part of
the fossa is formed by the orbital parts of the frontal bone, which support the frontal lobes of the brain and form the roofs of
the orbits. This surface shows sinuous impressions (brain markings) of the orbital gyri (ridges) of the frontal lobes.
The frontal crest is a median bony extension of the frontal bone. At its base is the foramen cecum of the frontal bone, which gives passage to vessels during fetal
development, but is insignificant postnatally. The crista galli (Latin cock's comb) is a thick, median ridge of bone posterior
to the foramen cecum, which projects superiorly from the
ethmoid. On each side of this ridge is the sieve-like cribriform plate of ethmoid bone. Its numerous tiny foramina transmit the olfactory nerves (CN I) from the olfactory areas
of the nasal cavities to the olfactory bulbs of the brain, which
lie on this plate.