Main Model

Renal pelvis
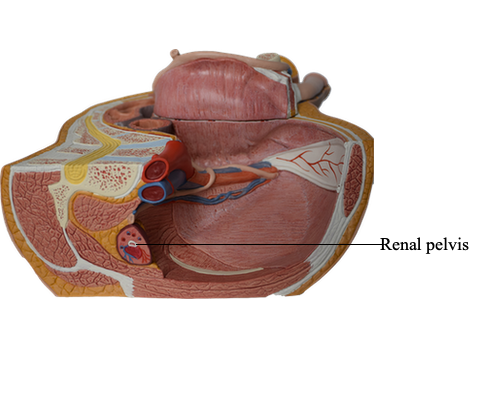
The renal pelvis is the flattened, funnel-shaped expansion of the superior end of the ureter. The apex of the renal pelvis is continuous with the ureter. The renal pelvis receives two or three major calices (calyces), each of which divides into two or three minor calices. Each minor calyx is indented by a renal papilla, the apex of the renal pyramid, from which the urine is excreted. In living persons, the renal pelvis and its calices are usually collapsed (empty). The pyramids and their associated cortex form the lobes of the kidney. The lobes are visible on the external surfaces of the kidneys in fetuses, and evidence of the lobes may persist for some time after birth.