Main Model

27 Ovarian artery
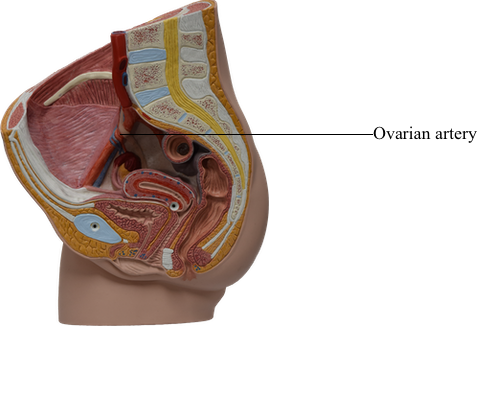
The ovarian arteries arise from the abdominal aorta and descend along the posterior abdominal wall. At the pelvic brim, they cross over the external iliac vessels and enter the suspensory ligaments, approaching the lateral aspects of the ovaries and uterine tubes. The ascending branches of the uterine arteries (branches of the internal iliac arteries) course along the lateral aspects of the uterus to approach the medial aspects of the ovaries and tubes. Both the ovarian and ascending uterine arteries terminate by bifurcating into ovarian and tubal branches, which supply the ovaries and tubes from opposite ends and anastomose with each other, providing a collateral circulation from abdominal and pelvic sources to both structures.