Main Model
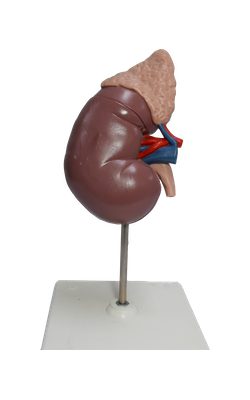
Renal vein

Several renal veins drain each kidney and unite in a
variable fashion to form the right and left renal veins; these veins
lie anterior to the right and left renal arteries. The longer left renal
vein receives the left suprarenal vein, the left gonadal (testicular or
ovarian) vein, and a communication with the ascending lumbar vein; it
then traverses the acute angle between the superior mesenteric artery
anteriorly and the aorta posteriorly. Each renal vein drains into the
inferior vena cava.