Main Model
Arcuate vein
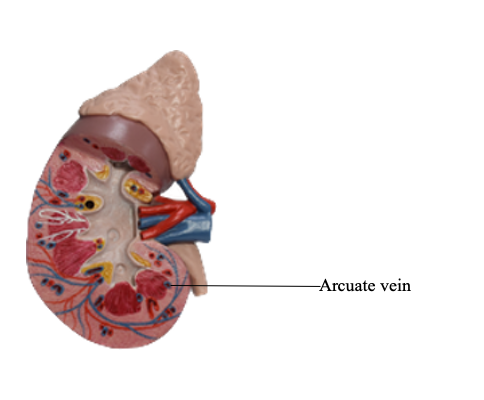
After entering the hilum, the renal artery ramifies
to form interlobar arteries, which run between the medullary pyramids.
At the corticomedullary junction, the interlobar arteries give rise to arcuate arteries,
which run parallel to the surface of the kidney. The interlobular
arteries, derived from the arcuate arteries, run between the medullary
rays toward the capsule. The interlobular arteries branch into several
afferent glomerular arterioles, which supply the capillaries of the
glomeruli. From there blood passes into the efferent glomerular
arterioles, which branch again to form a second capillary network,
supplying the majority of other portions of the same nephrons. The blood
is collected into the interlobular veins, which join the arcuate veins.
Then blood flows into the interlobar veins, which collectively form the
renal vein through which blood leaves the kidney.