Main Model
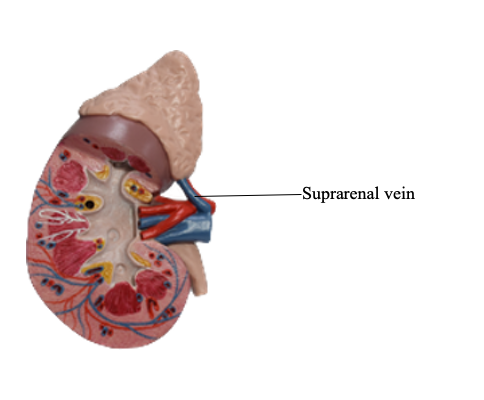
Suprarenal vein
The endocrine function of the suprarenal glands
makes their abundant blood supply necessary. The suprarenal arteries
branch freely before entering each gland so that 50–60 branches
penetrate the capsule covering the entire surface of the glands.
Suprarenal arteries arise from three sources:
• Superior suprarenal arteries from the inferior phrenic arteries
• Middle suprarenal arteries from the abdominal aorta near the level of origin of the superior mesenteric aorta
• Inferior suprarenal arteries from the renal arteries
• Superior suprarenal arteries from the inferior phrenic arteries
• Middle suprarenal arteries from the abdominal aorta near the level of origin of the superior mesenteric aorta
• Inferior suprarenal arteries from the renal arteries
The venous drainage of the suprarenal glands occurs via large suprarenal veins. The short right suprarenal vein drains into the inferior vena cava, whereas the longer left suprarenal vein, often joined by the inferior phrenic vein, empties into the left renal vein.