Main Model
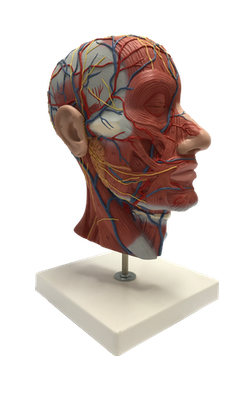
Brain : 1 Superior sagttal sinnus

The dural venous sinuses are endothelium-lined spaces between the periosteal and meningeal layers of the dura. They form where the dural septa attach along the free edge of the falx cerebri and in relation to formations of the cranial floor. Large veins from the surface of the brain empty into these sinuses and most of the blood from the brain ultimately drains through them into the internal jugular veins. The superior sagittal sinus lies in the convex attached border of the falx cerebri. It begins at the crista galli and ends near the internal occipital protuberance at the confluence of sinuses, a meeting place of the superior sagittal, straight, occipital, and transverse sinuses. The superior sagittal sinus receives the superior cerebral veins and communicates on each side through slit-like openings with the lateral venous lacunae, lateral expansions of the superior sagittal sinus.