Main Model

Osteocytes : View 1
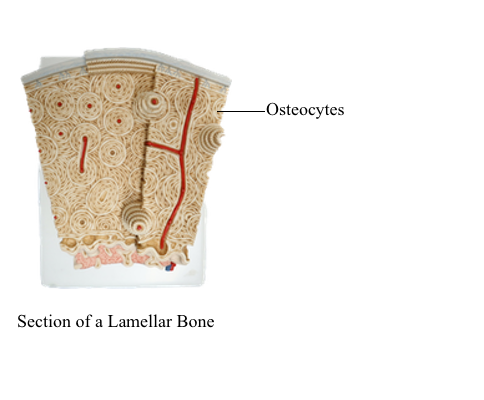
Bone (osseous tissue) is a specialized connective tissue with the property of marked rigidity and strength. Bone forms most of the skeleton of the body. It is composed of cells, osteocytes, and intercellular matrix, which contains an organic component, mainly collagen fibers, and an inorganic component including calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate. Lamella, the basic structure of bone, is composed of osteocytes and collagen fibers. Lamellae form both compact and spongy bone. Unlike cartilage, bone is supplied with blood vessels and nerves.
A Haversian system, or osteon, measuring 100-500 micrometer in diameter and several centimeters in length, consists of 4 to 20 layers of Haversian lamellae arranged concentrically and a Haversian canal, which is located in the center of the system. Between lamellae are irregular oval lacunae occupied by osteocytes. They communicate via fine canaliculi.