Main Model

Hepatocyte : Superior
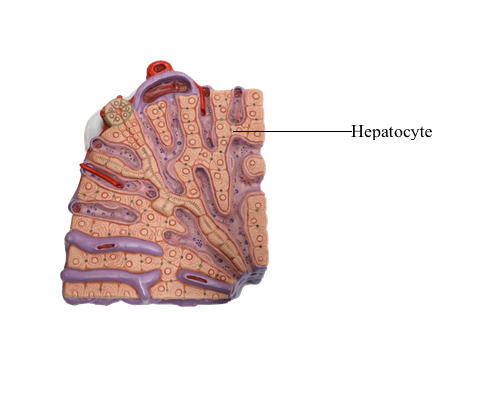
The hepatic lobule (liver lobule) is the structural unit of the liver; it is composed of parenchymal cells called the hepatocytes (hepatic cells), arranged in plates or cords that are interconnected with one another.
Large, polygonal hepatocytes form the hepatic plate. Their cytoplasm in H.E.-stained sections is eosinophilic; it is filled with granular structures which at the level of electron microscopy are identified as the mitochondria and lysosomes. The pale areas correspond with granular or agranular endoplasmic reticulum. Each hepatocyte has one or two nuclei, each with a conspicuous nucleolus. The hepatocytes are responsible for almost all the functions of the liver.