Main Model
CRANIUM : Superior view of cranium
Occipital Aspect of Cranium
The posterior or occipital aspect of the cranium is composed of the occiput (Latin back of head, the convex posterior protuberance of the squamous part of the occipital bone), parts of the parietal bones, and mastoid parts of the temporal bones.
The external occipital protuberance, is usually easily palpable in the median plane; however, occasionally (especially in females) it may be inconspicuous. A craniometric point defined by the tip of the external protuberance is the inion (Greek nape of neck). The external occipital crest descends from the protuberance toward the foramen magnum, the large opening in the basal part of the occipital bone.
The superior nuchal line, marking the superior limit of the neck, extends laterally from each side of the protuberance; the inferior nuchal line is less distinct. In the center of the occiput, lambda indicates the junction of the sagittal and the lambdoid sutures. Lambda can sometimes be felt as a depression. One or more sutural bones (accessory bones) may be located at lambda or near the mastoid process.
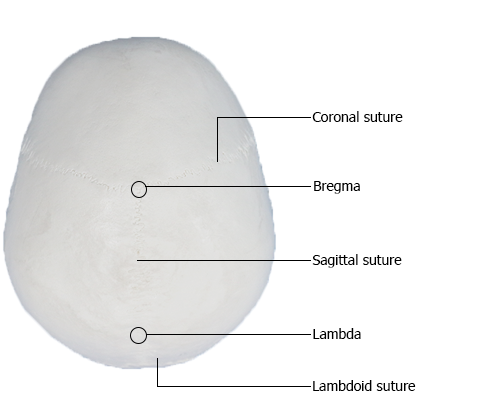
Superior Aspect of Cranium
The superior (vertical) aspect of the cranium, usually
some what oval in form, broadens posterolaterally at the parietal eminences. In some people, frontal eminences are also visible, giving the calvaria an almost square
appearance.
The coronal suture separates the frontal and parietal
bones, the sagittal suture separates the parietal bones, and the lambdoid suture separates the parietal
and temporal bones from the occipital bone. Bregma is the craniometric landmark formed by the intersection of the sagittal and coronal sutures. Vertex, the most superior point of the calvaria, is
near the midpoint of the sagittal suture.
The parietal foramen is a small, inconstant aperture
located posteriorly in the parietal bone near the sagittal
suture; paired parietal foramina may be present. Most irregular, highly variable foramina that occur in the
neurocranium are emissary foramina that transmit emissary veins connecting scalp veins to the venous sinuses of the dura
mater.