Main Model
Cranial Nerves : IV Trochlear nerve
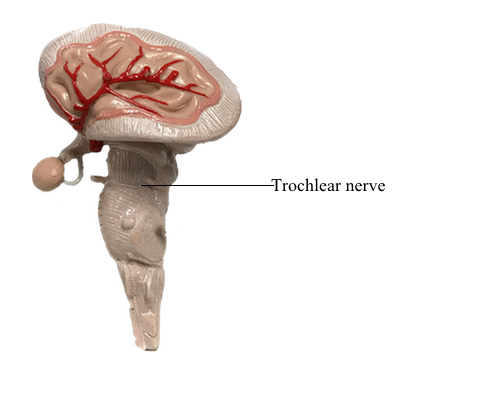
Trochlear Nerve (CN IV)
Functions: Somatic motor (general somatic efferent) to one extra-ocular muscle (superior oblique).
Nucleus: The nucleus of the trochlear nerve is located in the midbrain, immediately caudal to the oculomotor nucleus.
The trochlear nerve (CN IV) is the smallest cranial nerve. It emerges from the posterior (dorsal) surface of the midbrain (the only cranial nerve to do so), passing anteriorly around the brainstem. It has the longest intracranial (subarachnoid) course of the cranial nerves. The trochlear nerve pierces the dura mater at the margin of the tentorium cerebelli, and passes anteriorly in the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus. CN IV then continues through the superior orbital fissure into the orbit, where it supplies the superior oblique - the only extra-ocular muscle that uses a pulley, or trochlea, to redirect its line of action (hence the nerve's name).