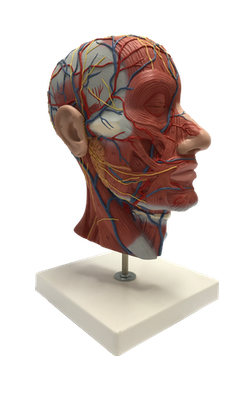
Main Model
Bones : a Frontal sinus
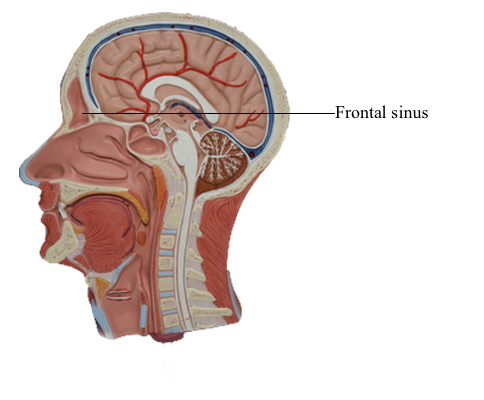
The right and left frontal sinuses are between the outer and inner tables of the frontal bone, posterior to the superciliary arches and the root of the nose. Frontal sinuses are usually detectable in children by 7 years of age. The right and left sinuses each drain through a frontonasal duct into the ethmoidal infundibulum, which opens into the semilunar hiatus of the middle nasal meatus. The frontal sinuses are innervated by branches of the supra-orbital nerves (CN V1).
The right and left frontal sinuses are rarely of equal size, and the septum between them is not usually situated entirely in the median plane. The frontal sinuses vary in size from approximately 5 mm to large spaces extending laterally into the greater wings of the sphenoid. Often a frontal sinus has two parts: a vertical part in the squamous part of the frontal bone, and a horizontal part in the orbital part of the frontal bone. One or both parts may be large or small. When the supra-orbital part is large, its roof forms the floor of the anterior cranial fossa and its floor forms the roof of the orbit.